Elements code tutorial
Desktop application example in Python
In this example we will be using Python to make an RPC (Remote Procedure Call) to the Elements daemon (elementsd). This was what the Elements client (elements-cli) application was doing when we executed commands in the main section of the tutorial. Any language that supports making http requests could be used. You can check if Python is installed on your system by following the steps here. We’ll assume you are running Python3.
Our aim is simply to make a call to elementsd using RPC by executing some basic Python code. We will be using the popular AuthServiceProxy Python JSON-RPC interface to handle the connection, authentication and data typing for us as we communicate with our node. We’ll also use virtualenv to create an isolated environment to run our code in.
First we will need to install a few prerequisites. From the terminal run the following commands one after another:
sudo apt-get install python3-pip
sudo pip3 install virtualenv
Create a directory named ‘elementstutorialpython’ and move into it:
cd
mkdir elementstutorialpython
cd elementstutorialpython
Set up and Activate virtualenv in that directory:
virtualenv venv
source venv/bin/activate
Use pip to install python-bitcoinrpc within the environment:
pip3 install python-bitcoinrpc
That will have set up all we need to run our Python tutorial code.
Create a new file named elementstutorial.py in the ‘elementstutorialpython’ directory and paste the code below into it.
from __future__ import print_function
from bitcoinrpc.authproxy import AuthServiceProxy, JSONRPCException
rpc_port = 18884
rpc_user = 'user1'
rpc_password = 'password1'
try:
rpc_connection = AuthServiceProxy("http://%s:%s@127.0.0.1:%s"%(rpc_user, rpc_password, rpc_port))
result = rpc_connection.getwalletinfo()
print(result["balance"]["bitcoin"])
except JSONRPCException as json_exception:
print("A JSON RPC Exception occured: " + str(json_exception))
except Exception as general_exception:
print("An Exception occured: " + str(general_exception))
The code defines the details needed to connect to the elementsd node using RPC commands, sets up the method we want to execute and the parameter we want to pass in, executes the call and prints out the “balance” value from the results.
Before we try running the code make sure the required bitcoin and elements daemons are running.
NOTE: If you get an error connecting to the elements client when you run the code below it may be because your node has been left in an altered state after quitting the tutorial code at an early stage. To refresh and reset the daemon’s blockchain and config files re-run the first section of the tutorial code up to and including the lines where the 3 config files are copied into the new directories, then run the commands above to start the required daemons.
To run our Python code execute the following command:
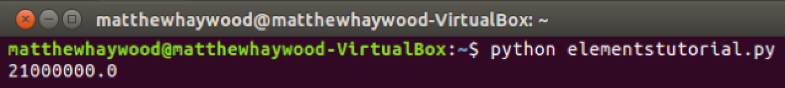
python3 elementstutorial.py
The result of which should be:
When you have finished, deactivate virtualenv:
deactivate
When you want to run your code again, activate the environment from within the ‘elementstutorialpython’ directory, run the code and then deactivate when finished:
source venv/bin/activate
python3 liquidrpcpython.py
deactivate
Obviously that’s a very basic example but you now have a functioning setup which you can use as a building block for further development. The next tutorial section takes the code above and implements it within a web application using Flask.
